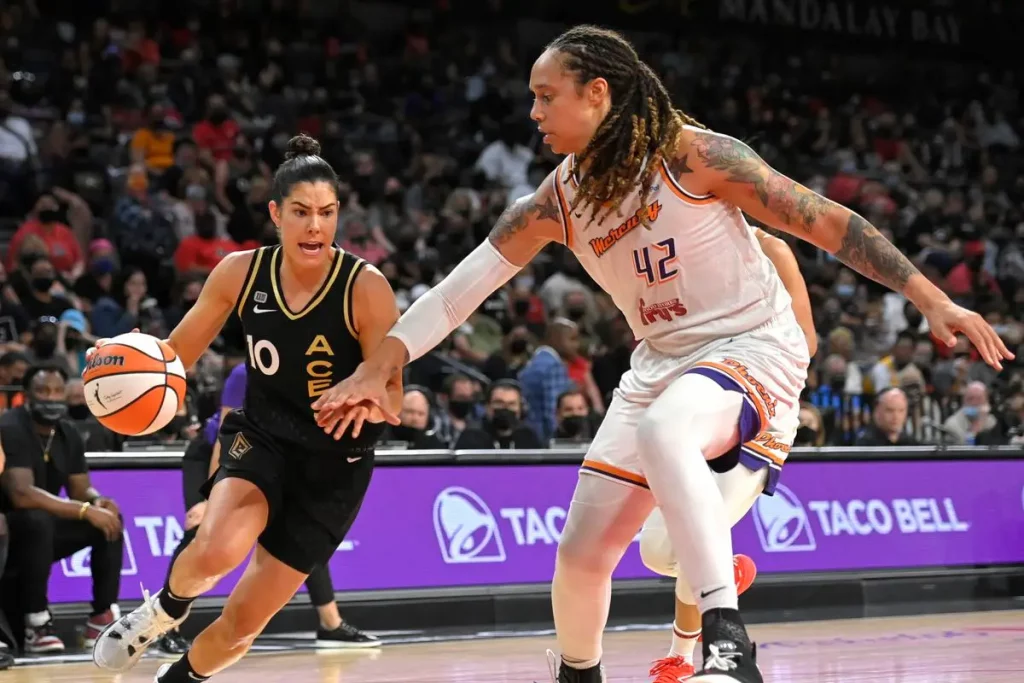Two Frontlines, One Battle
The Las Vegas Aces and the Phoenix Mercury are locked in a heated championship duel, a rivalry that pits reigning dominance against historic grit. Yet beyond the hardwood, both teams—and every player in the WNBA—are facing an opponent far more consequential than any finals matchup. By October 31, players and league leadership must agree on a new collective bargaining agreement (CBA), one that will determine the financial structure, working conditions, and trajectory of women’s basketball for years to come.
At stake is more than salary increments; it is about recognition, sustainability, and a share of the booming revenues the WNBA is finally beginning to generate. With viewership rising, merchandise selling out, and media rights expanding, players argue that they deserve a proportionate slice of the pie. The CBA negotiations are no less than a referendum on the future of professional women’s sports.
The Championship Spotlight: On-Court Fireworks
The finals themselves could not be scripted better. The Las Vegas Aces, reigning champions, are powered by A’ja Wilson’s dominance and Chelsea Gray’s orchestration. Across the floor stand the Phoenix Mercury, an iconic franchise rejuvenated by Brittney Griner’s return and Diana Taurasi’s veteran leadership.
The clash captures two narratives: Las Vegas as the league’s new epicenter of glamour, investment, and ambition; Phoenix as the standard-bearer of WNBA resilience and tradition. These games symbolize not only sporting glory but also the broader stakes of visibility. Every nationally televised game is a showcase for what the WNBA has become: fast-paced, marketable, and culturally resonant.
View this post on Instagram
Rising Revenues, Stagnant Distribution
Behind the spotlight, however, lies the crux of the CBA debate. The WNBA has experienced a surge in growth:
-
Viewership: The 2023 season broke records with double-digit percentage increases in national TV audiences.
-
Sponsorships: Companies like Nike, Google, and Coinbase have aligned with the league.
-
Merchandise: Jersey and sneaker drops tied to stars like Wilson, Griner, and Sabrina Ionescu have sold out within hours.
-
Expansion: A new Bay Area team is on the horizon for 2026, signaling investor confidence.
Yet despite these gains, the average player salary hovers around $120,000, with top earners reaching $250,000—figures dwarfed by the NBA’s minimum contracts. The union’s central demand is a larger percentage of league revenue, moving closer to the 50-50 revenue split seen in the NBA. Currently, WNBA players reportedly receive less than 20% of league-generated income.
A Union United
The WNBA Players Association (WNBPA), led by Nneka Ogwumike until recently and now under a renewed leadership structure, has sharpened its strategy. Unlike earlier eras when players prioritized basic improvements—better travel, maternity protections, and training resources—the union now has leverage through visibility and public opinion.
The success of the U.S. Women’s National Soccer Team’s equal pay fight has emboldened WNBA players. Social media has become a weapon; stars like Wilson, Taurasi, and Breanna Stewart can amplify their messages directly to millions. The central rallying cry is fairness: if the league markets players as global stars, then compensation must reflect that role.
The Owners’ Perspective
League leadership and team owners acknowledge the momentum but argue for caution. Their position is that while revenues are growing, profitability remains fragile. The WNBA, they note, still requires subsidies from the NBA in several areas, and expanding salaries too rapidly could destabilize finances.
Yet critics point out that this logic mirrors past arguments used in men’s sports, where eventual leaps in investment spurred growth rather than hindered it. In essence, the players are challenging owners to bet on the league’s future rather than guard its present.
The Economics of Respect
The debate is not purely financial; it is symbolic. For decades, WNBA players have contended with second-class treatment: cramped charter restrictions, inconsistent broadcast deals, and limited marketing. The current CBA negotiations are about rewriting that history.
Players want:
-
Revenue Sharing: A guarantee of a fixed percentage of all league income.
-
Full-Time Charters: Ending the disparity of commercial flights.
-
Increased Minimums: Ensuring rookies and bench players earn livable wages.
-
Equity Stakes: Exploring ownership shares as part of long-term deals.
For the players, these demands represent dignity as much as dollars.
Culture
The WNBA occupies a unique cultural role. It is not just a league but a symbol of representation—women excelling in a space historically dominated by men. Stars like Taurasi and Griner have become advocates for social justice, LGBTQ+ rights, and racial equity.
Thus, the CBA is not simply a labor negotiation. It is a platform for women athletes to assert their worth in a society where gender pay disparities persist across industries. A successful deal could ripple outward, influencing other women’s leagues—from soccer to hockey to volleyball.
Lessons from Other Sports
The WNBA is not negotiating in a vacuum. Two precedents loom large:
-
The USWNT Equal Pay Settlement (2022): The U.S. women’s soccer team secured a landmark deal for equal pay and prize money distribution. Their victory shifted cultural expectations.
-
NBA’s Own CBA Evolution: Decades ago, NBA players also earned modest wages. It was only through persistent union negotiations and the league’s belief in its stars that modern salaries skyrocketed.
For WNBA players, the message is clear: today’s sacrifices must yield tomorrow’s security.
Fans and Public Opinion
Public sentiment is increasingly on the players’ side. Social media amplifies calls for equity, while celebrities and NBA stars—from LeBron James to Steph Curry—have lent their voices. Attendance at arenas like Michelob Ultra Arena in Las Vegas demonstrates that demand exists when games are marketed effectively.
The CBA fight is thus not confined to boardrooms. Fans recognize their role: purchasing tickets, streaming games, and amplifying the message that women’s basketball deserves investment.
No comments yet.